Gaze control
The goal of this task is to implement gaze controller for the iCub robot that is able to follow a ball moving on a table.
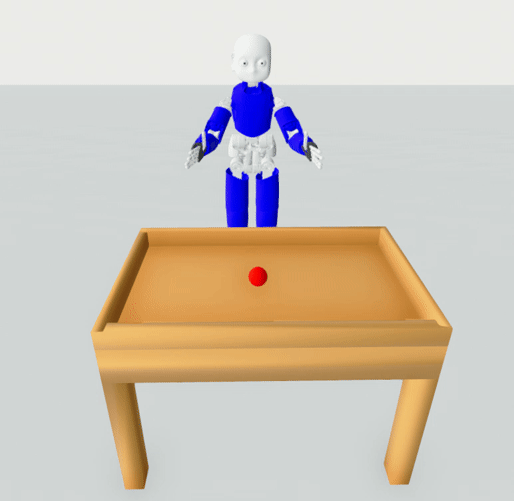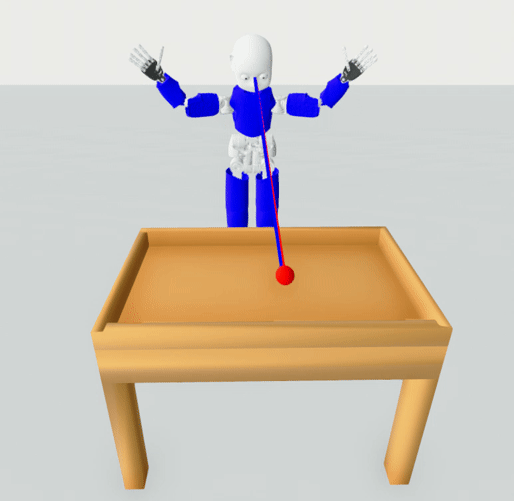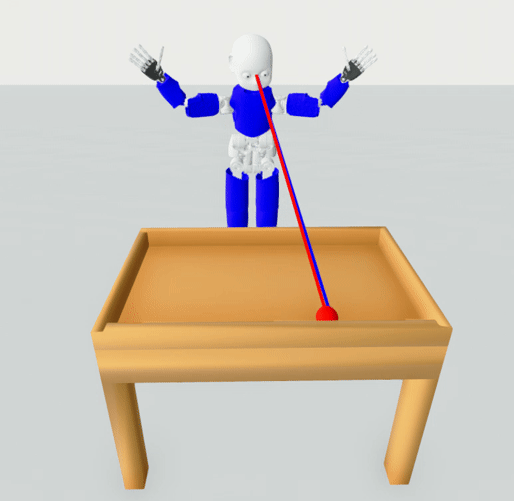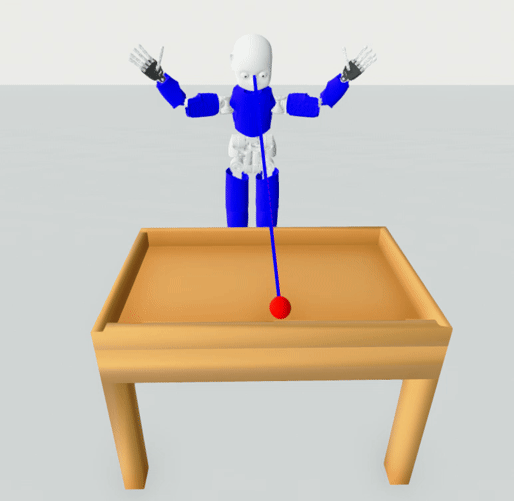
The task is simplified to 2D case, i.e., the ball can move in x and y. The user is given the vector from
the head to a ball (the where the robot should look) and the vector where the robot is looking right now.
Task
Implement gaze() function in exercise_3.py that will control the gaze of the robot to follow the ball.
the function takes three arguments:
client - instance of pycub class that controls the simulation
head_direction - normalized vector representing the view of the robot, i.e., where the robot is looking
head_ball_direction - normalized vector representing the direction from the robot to the ball, i.e., where the robot should be looking
the function should control joints in the necks of the robot to follow the ball
the move must non-blocking, i.e., parameter wait=False
you should not call
update_simulation()in this function
Scoring
the ball will be moving for 10 (default) seconds and each step the error in degrees will be calculated
maximum number of points is 10 (default; 10 runs of the code) and you can lose points for individual runs based on the following:
if the mean absolute error is:
less than 0.5 degree - 0% of points
more than 0.5 and less than 1 degree - 50% of points
more than 1 and less than 5 degrees - 75% of points
more than 5 - 100% of points
if the max error is:
less than 2 degrees - 0% of points
more than 2 and less than 5 degrees - 25% of points
more than 5 and less than 10 degrees - 50% of points
more than 10 - 100% of points
the loss is accumulated for both mean and max error, e.g., 75% loss in mean and 25% in max means 100% and 0 points
Requirements
Those apply mainly for exercise_3_tester.py to work correctly:
do not create new client instance, use the one that is passed as an argument
do not rename the function or file
use non-blocking movements, i.e., use parameter wait=False or use velocity control
do not call
update_simulation()in any of your code
Those apply so that you fulfill the exercise as intended:
Do not turn of gravity